The Fusion Splicer: A Brief Introduction
In today’s rapidly advancing world of telecommunications and networking, the demand for reliable and efficient fiber optic connections has never been higher. At the heart of these connections, Fusion Splicers play a key role in making sure these streams of communication are seamless and efficient. For this reason, whether you're a seasoned technician or new to the field, understanding the function and types of fusion splicers is essential for ensuring optimal network performance.
1. What is a Fusion Splicer?

A fusion splicer is a specialized device used to join two optical fibers end-to-end through the process of fusion. By aligning the fibers precisely and applying a controlled electric arc, the fusion splicer melts the ends of the fibers, creating a single, continuous fiber. This process minimizes signal loss and reflection, resulting in a strong, reliable connection that is almost indistinguishable from a continuous piece of fiber.
2. How Does a Fusion Splicer Work?

Preparation: Before splicing, the optical fibers must be carefully stripped of their outer jackets and protective polymer coatings using a wire stripper and kevlar cutter. Once stripped, they must be thoroughly cleaned and precisely cleaved to create smooth, perpendicular end faces.
Alignment: The fusion splicer utilizes precise motors and optical systems to align the fiber cores. This ensures that the final splice is as seamless as possible, reducing attenuation. Technicians can monitor the alignment using an optical power meter, video camera, or viewing scope.
Impurity Burn-Off: Even after manual cleaning, traces of dust or moisture can remain on the fibers. To ensure a high-quality splice, the fusion splicer generates a small pre-fusion spark to burn off any remaining contaminants.
Fusion: The fusion splicer then generates a controlled, high-temperature arc to melt and fuse the fiber ends together. This process ensures that the cladding and core remain distinct, minimizing optical loss. The resulting splice is then tested for insertion loss, with most fusion splices achieving an optical loss of 0.1 dB or less.
3. Types of Fusion Splicers
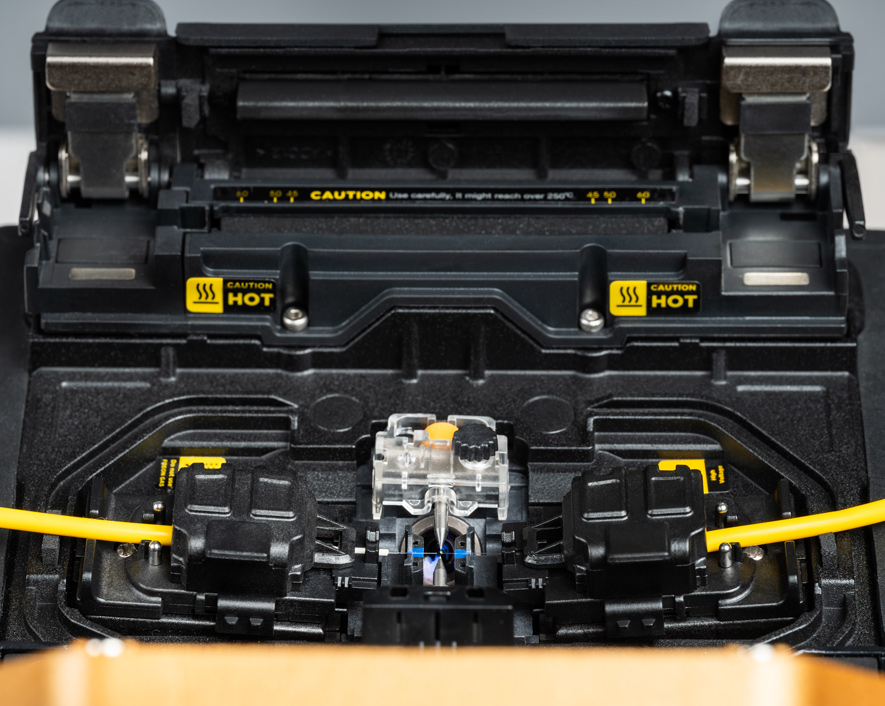
There are three main types of fusion splicer: Core, Cladding, and Ribbon Fusion Splicers. These Fusion Splicers vary in terms of alignment, precision, and the number of fiber they work with.
Core Alignment Fusion Splicers
Core alignment splicers use advanced imaging systems and six motors to align the fiber cores with high precision. These splicers rely on high-resolution cameras and multiple-axis movement to ensure optimal core matching, reducing insertion loss to a minimum. This type is ideal for applications requiring minimal signal loss, such as long-haul networks, high-performance telecommunications, and data centers. Due to their high accuracy, they are often the preferred choice for critical infrastructure project.
Cladding Alignment Fusion Splicers
Cladding alignment splicers are more cost-effective than core alignment splicers and align fibers by their outer cladding rather than the core itself. These splicers use fixed V-groove alignments to bring the fibers into position, making them less precise than core fusion splicers. While they may result in slightly higher signal loss than core alignment splicers, they are still highly effective for less demanding applications, such as local area networks (LANs), fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) installations, and temporary or emergency fiber optic repairs.
Ribbon Fiber Fusion Splicers
Ribbon fiber splicers are designed to splice multiple fibers simultaneously, making them ideal for high-density fiber applications. These splicers can up to 12 fibers at once, significantly reducing splicing time and increasing efficiency for large-scale deployments. They are commonly used in metro networks, data centers, and backbone installations where speed and precision are essential. Ribbon fusion splicers use specialized holders and software algorithms to ensure proper alignment and fusion of all fibers in the ribbon, reducing overall labor costs and improving consistency in mass fiber splicing.
4. Conclusion
Fusion splicers are indispensable tools in the fiber optic industry, enabling efficient and reliable network connections. Understanding the different types of fusion splicers and their applications empowers technicians to select the right tool for the job, ensuring robust and high-quality fiber optic installations. As technology continues to advance, the role of the fusion splicer remains a cornerstone in building the networks that keep us all connected!

Comments
Login or Register to post comments.