Simple Steps on How to Use Visual Fault Locators
Simple Steps on How to Use Visual Fault Locators
Fiber optic cables are an essential component of modern communication systems, delivering high-speed data transfer and reliable connectivity. However, fiber optic cables can develop faults due to a range of factors, such as improper installation, accidental damage, or wear and tear. Finding and fixing these faults can be challenging, especially when dealing with long cables or complex networks.
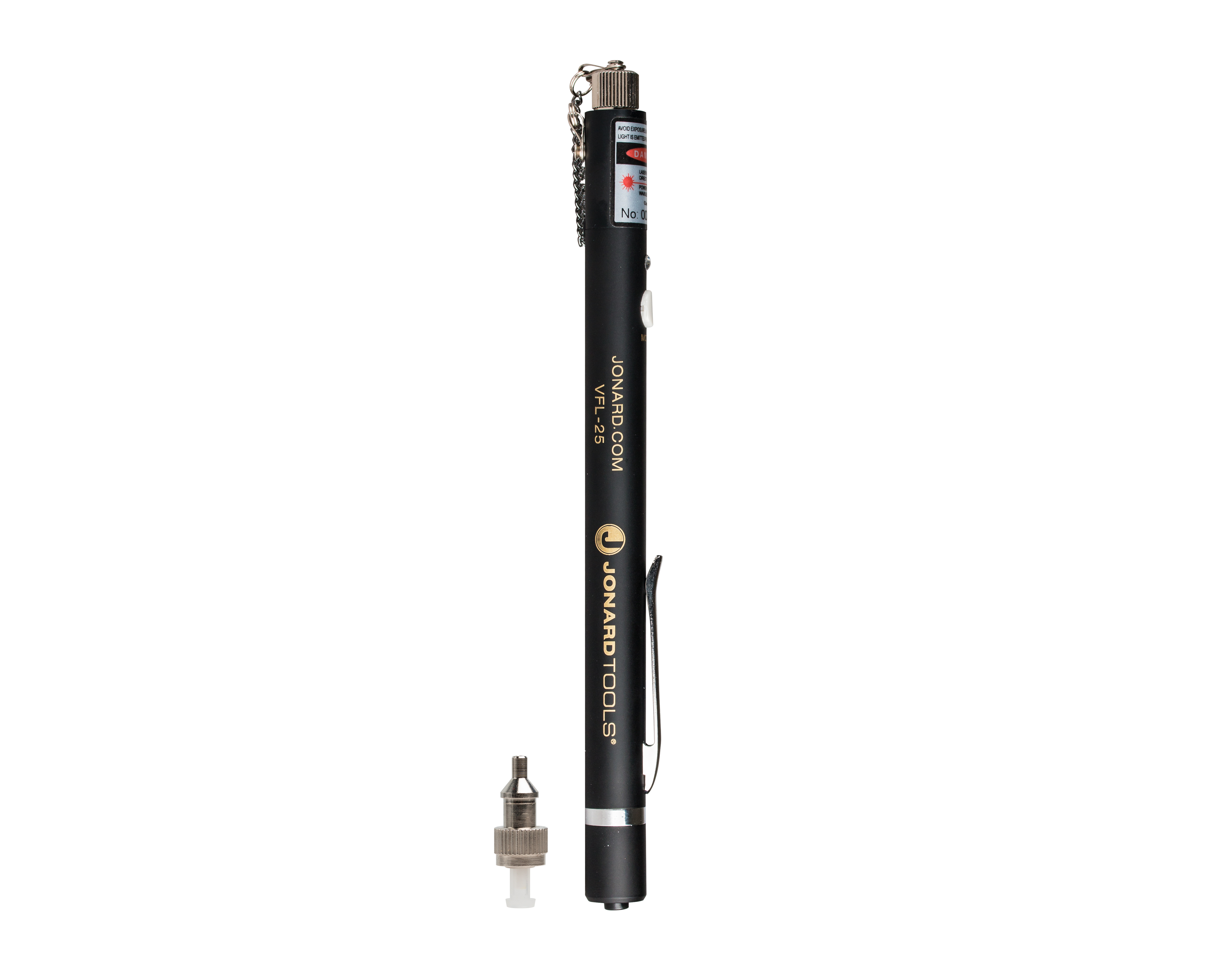

Fortunately, visual fault locators (VFLs) can help technicians quickly identify the location of faults in fiber optic cables. VFLs use a laser beam to generate visible light that travels through the cable, illuminating any breaks or faults in the fiber. One such visual fault locator, the Jonard Tools VFL-25, is the perfect tool for inspecting and troubleshooting fiber networks. It is designed for field personnel who need a portable light source for fiber tracing, fiber routing, and to locate breakpoints caused by bending or cracking in fiber optic cables and poor connections.
The VFL-25 Visual Fault Locator and the VFL-150 Fault Locator Kit (includes the VFL-25 Visual Fault Locator and the VFL-25125 FC to LC Adapter) are the go-to tools for examining fiber optic patch cords, ribbon or bunched pig tails. Visual fault locators are also commonly used for testing fiber optic networks, telecommunications and CATV fields. It is an indispensable tool in fiber cable network construction, fiber network maintenance and optical component manufacturing and research. The VFL-25 Class IIIa laser emits a red laser to inspect for fiber failure. It should be noted that visual fault locators generally are not suitable for work on dark or shielded cables.

- Unscrew power switch cap, install batteries. Note: The cathode (1) of the batteries must point toward the power switch cap. Screw power switch cap back in place. Unscrew dust cap, press the power switch on the end of the cap to power up unit.
- Press the mode switch to activate laser in continuous mode. A continuous red beam will emanate from the VFL-25 at the 2.5mm universal connector.
- Press mode switch again and the red beam will pulse (frequency 6-9 Hz).
- Press mode switch again the beam will pulse at a slower rate (frequency 1-2 Hz).
- Press the mode switch once more to shut off laser.
- To test a cable, insert the cable with either a SC, ST or FC connector on the end into the 2.5mm universal connector. Press the mode switch to select continuous mode or pulsed mode.
- When finished press the mode switch to shut off the red beam. Press the power switch to power down the unit and screw on dust cap.
- If the unit sits for extended periods of time, the removal of batteries is recommended to prevent damage from occurring to the VFL-25 due to battery leakage.
Using fiber optic visual fault locators are effective, fast and easy. By following these simple steps you can quickly locate breaks or faults in your fiber optic network and take the necessary steps to repair them. For additional support, please view the below VFL video demonstration.
About Jonard Tools:
Founded in 1958, Jonard Tools® manufactures tools for the Telecom, CATV, Fiber Optic, Home Automation, Security & Alarm, and Electrical markets. Jonard Tools designs and engineers patented products by utilizing customer partnerships to create innovative solutions for industry needs. New tools are released each month and are all Made For Life® with lifetime warranties. Through quality and innovation Jonard aims to move the industry forward and connect the world.
Lifetime Warranty
Our tools are designed and engineered with quality materials that are Made For Life®.

Comments
Login or Register to post comments.